
How to check your cable modem health - diagnostics, power levels, S/N ratio
This is the industry standard address for a cable modem. Most cable companies allow you to look at the cable modem, but will not let you change anything. If your cable company allows this, you should see a page come up similar to the one below. Depending on your equipment, your screen could look VERY different.
You may need to click around a little bit to find these THREE things:
Downstream Power - measured in dBmV
Signal to Noise Ratio (or S/N) - measured in dB
Upstream Power - measured in dBmV
They are highlighted in the window below.
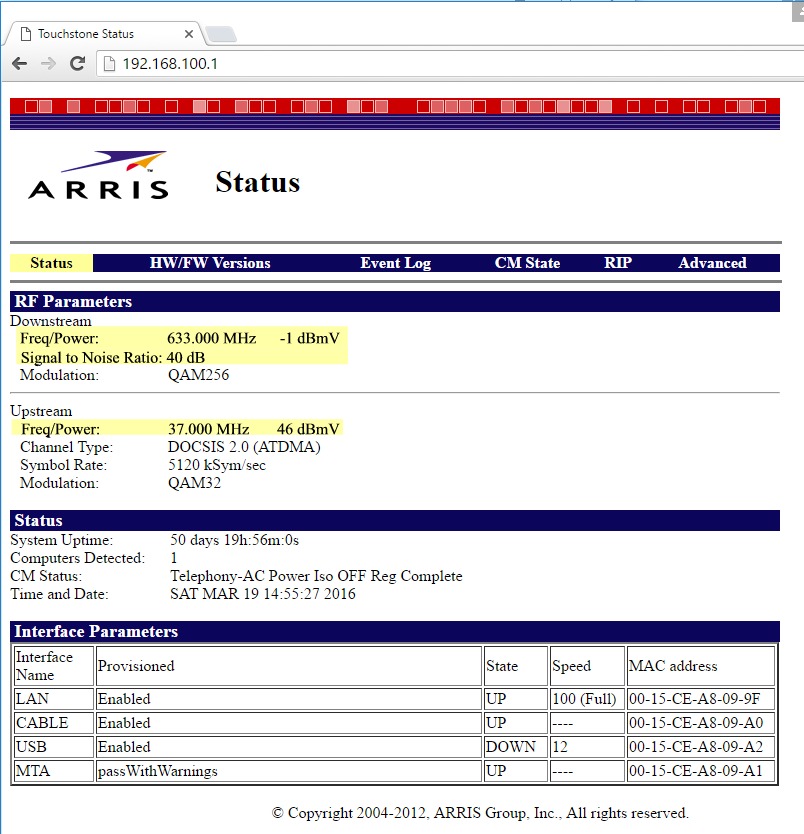
Q: What am I looking at?
For diagnostic purposes, the cable modem measures and reports key information. Some of these are the Downstream Received Power and the Downstream Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR), and Upstream Power Level. The Signal-to-Noise Ratio is an indicator of how "clean" your signal is when the cable modem receives it. A high Signal-to-Noise Ratio indicates that the signal can be readily decoded, and information can be extracted without excessive errors. Even if the power level is high enough, your cable modem may have problems receiving data if the S/N Ratio is too low.
Q: What is the difference between downstream and upstream?Upstream power levels give you an idea of how much power the cable modem needs to use to communicate back to the cable company. It is pretty much the only indicator you have of any potential issues which affect your cable modem or cable boxes (when they use interactive services or On Demand). Upstream Power Level is an indicator of how hard the cable modem has to work in order to get the signal back to the cable company's headend. The cable modem's Upstream Power Level is actually set by commands from the headend so that the headend hears relatively the same signal level from all cable modems on that particular upstream channel ID. Since every cable modem is at a different distance from the headend, they will each have different return path signal characteristics - mainly the signal loss due to the cable length. In addition, the wiring inside every home may be different, and the point of installation for the cable modem makes a difference in the return path losses.
Downstream is the the signal coming INTO your home from the cable company. There are only 2 measures of this signal - the absolute signal level (which is supposed to be in a FCC defined range at your main connection point) and the Signal to Noise Ratio. Generally the signal from the cable company should measure around 0dBmV at the point where the connection hits your house. After that it can change based on your cabling and splitters.
What are desirable signal levels?
Downstream Signal to Noise
(S/N) Ratio
50-1000MHz (Forward Path) Range: Above 25
Signal to Noise Ratios below 30 can indicate signal strength
problems. Anything above 30 should not give you any problems. In the
range of 30 or below, you could need a forward path boost. Look at the return
path signals to determine if you need an active return amplifier.
Downstream Power Level 50-1000MHz (Forward Path) Range:
-15 to +15dBmV
Signal levels at either end of the range may be problematic.
Generally you will not find signal levels that are too high unless you
already have an amplifier installed. Signal levels lower than -10dBmV
may indicate the need for an amplifier. If higher than -10dBmV, it
should generally be OK.
Upstream Power Level 5-42 MHz (Return Path) Range: +8 to
+58dBmV
Below 50, the cable modem is generally operating at a normal level.
Above 50, the cable modem is operating at the higher end of it's power
range. At 58dBmV the cable modem is "screaming" and not operating at an
optimal level. Levels above 50 indicate that an Active Return amplifier
will likely help. Levels above 55 - an Active Return amplifier is highly
recommended. Active Return amps:
PCT-VC9U
PCT-MAB-1015-1A
PCT-MAB-1015-4A
ARRIS BDA-42-1-AR-R
ARRIS BDA-42-4-AR-R